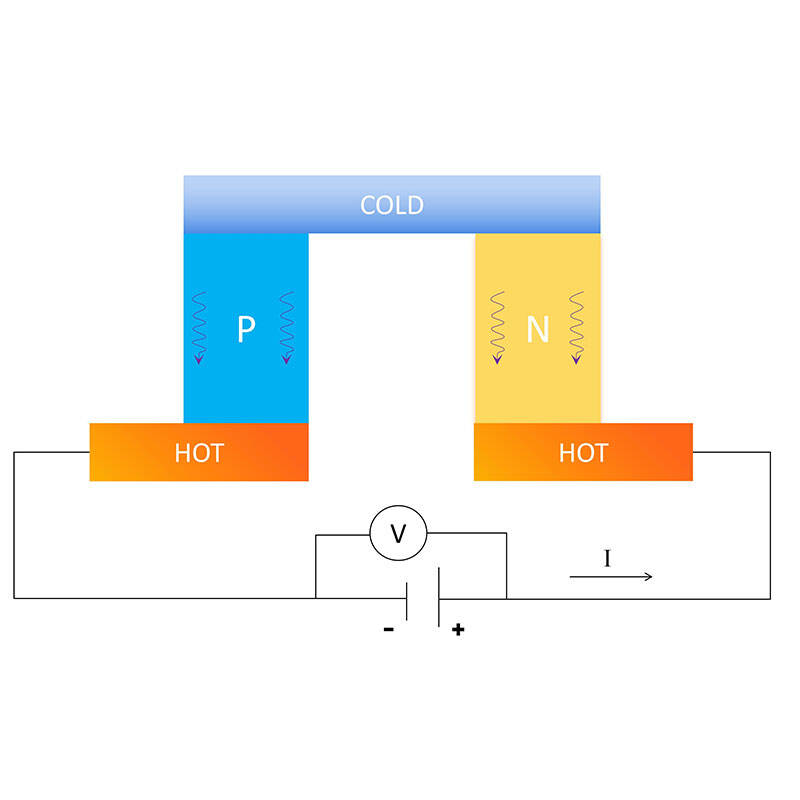
Scientific-grade CCD imaging is fundamentally constrained by thermal effects.Long exposure times are required to capture weak optical signals,but thermally generated dark current accumulates simultaneously,leading to:
1.Elevated noise floor
2.Reduced signal-to-noise ratio(SNR)
3.Limited dynamic range
4.Poor repeatability in calibration and measurements
Lowering and stabilizing the CCD operating temperature is the most effective way to suppress these limitations.
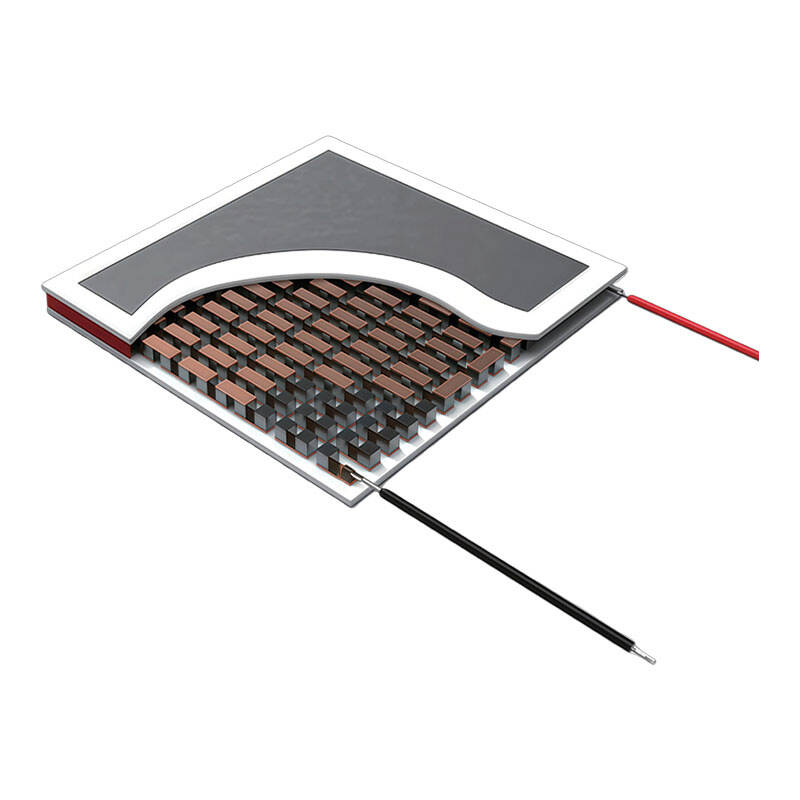
By actively controlling the CCD temperature between-30℃and-100℃,TEC cooling delivers measurable and repeatable performance improvements:
1.Dark current reduced by 100-1000×compared to room temperature
2.SNR increased from~10:1 to>1000:1
3.Dynamic range expanded from 12-bit to 16-bit or higher
4.Exposure time extended from minutes to hours
5.Stable gain,linearity,and dark-field characteristics over time
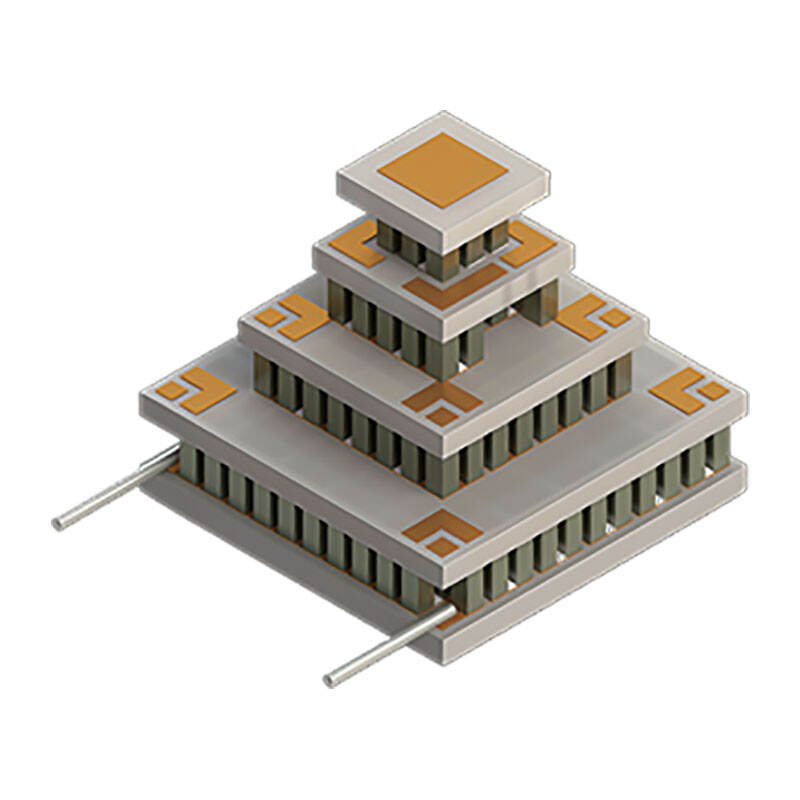
1.Solid-state design,no moving parts→long-term reliability
2.Zero vibration operation→no image blur or mechanical disturbance
3.Ultra-precise temperature control(±0.01℃typical)→stable photoelectric response
4.Compact,camera-head integrable form factor→supports miniaturization
5.Balanced cost,power consumption,and maintenance compared with cryo-genic alternatives
The following models represent typical multi-stage TEC models commonly used in CCD applica-tions.They are provided for reference and comparison only,not as a complete product list.

| TEC model | Imax(A) | dTmax(*C) | Qcmax(W) | Umax(V) | ACR(ohm) | Top(mm) | Bottom(mm) | Height(mm) |
| 4ITEC-107- 060208/122 | 1.3 | 116 | 1.2 | 6.6 | 4.9 | 8x8 | 9x9 | 6.6±0.1 |
| Th=27° C& Vac | ||||||||
| TEC model | Imax(A) | dTmax(°C) | Qcmax(W) | Umax(V) | ACR(ohm) | Top(mm) | Bottom(mm) | Height(mm) |
| 5iTEC-366- 211020 | 6.2 | 132.5 | 5.9 | 20.42 | 3.27 | 13.4x10.3 | 62x62 | 19±0.35 |
| Th=25° C& Vact | ||||||||